Development of mucoadhesive cationic polypeptide micelles for sustained cabozantinib release and inhibition of corneal neovascularization
Abstract
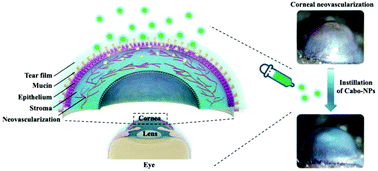
Corneal neovascularization (CNV) is one of the leading risk factors for vision loss. Anti-angiogenic drugs can theoretically be extended to the treatment of CNV. However, the application of these drugs is often hindered by traditional administration methods, e.g., eye drops, which is ascribed to the unique structure of the cornea and tear film. In this study, cationic polypeptide nanoparticles with mucoadhesive ability that carry lipophilic cabozantinib (a tyrosine kinase inhibitor), called Cabo-NPs, were developed for sustained cabozantinib release and inhibition of CNV. The polypeptides were synthesized via N-carboxyanhydride ring-opening polymerization and could self-assemble into micelles with cabozantinib in aqueous solution. The Cabo-NPs possessed good biocompatibility both in corneal epithelial cells and mouse corneas. More importantly, in vitro angiogenesis assays demonstrated the strong inhibitory effect of Cabo-NPs on cell migration and tube formation. Furthermore, the Cabo-NPs exerted superior anti-angiogenic effects with remarkable reductions in the neovascular area, which were as effective as the clinical dexamethasone but without apparent side effects. The therapeutic mechanism of the Cabo-NPs is closely related to the significant decrease in proangiogenic and proinflammatory factors, suppressing neovascularization and inflammation. Overall, cationic Cabo-NPs offer a new prospect for safe and effective CNV treatment via enhancing the bioavailability of lipophilic cabozantinib.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...