Multi-stimuli-responsive nanomicelles fabricated using synthetic polymer polylysine conjugates for tumor microenvironment dependent drug delivery†
Abstract
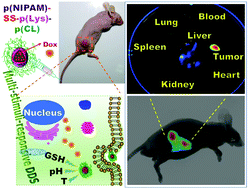
A series of multi-stimuli-responsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)30-SS-block-poly(L-lysine)30-block-poly(caprolactone)n (p(NIPAM)30-SS-b-p(Lys)30-b-p(CL)n) (n = 50, 75, 100, 125) triblock copolymers have been synthesized by combining reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer polymerization of NIPAM, organo-catalyzed ring-opening polymerization (ROP) of Z-lysine N-carboxyanhydride and metal-catalyzed ROP of CL with an azide–alkyne click reaction. The pH-responsive p(Lys) and temperature-responsive p(NIPAM) blocks are tethered by a redox-responsive disulfide linker and biodegradable p(CL) blocks with different lengths are also combined to tune the lower critical solution temperature and drug loading capacity of the resulting polymers. Highly uniform micelles with ∼200 nm size were fabricated by the self-assembly of the resultant copolymers in the presence of doxorubicin (Dox) with a high Dox encapsulation efficiency of around 50%. The combination of the enhanced permeability and retention effect with pH-, temperature- and redox-sensitive tumor microenvironment-responsive drug delivery of the nanomicelles endows them with cell internalization capability for the successful antitumor efficiency. Interestingly, this multi-stimuli-responsive platform makes a distinction from the conventional block copolymer systems by demonstrating fascinating tumor targeting without utilizing any targeting moiety. Thus, the easily accessible multi-stimuli-responsive triblock copolymer can be a promising theranostic system for intracellular drug delivery.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...