Encapsulated DNase improving the killing efficiency of antibiotics in staphylococcal biofilms†
Abstract
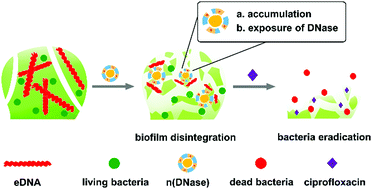
We developed a polymer-encapsulated DNase, n(DNase), which can efficiently accumulate in biofilm and expose the DNase to cleave the eDNA of the biofilm. CLSM and crystal violet staining results demonstrated effective biofilm disintegration (92.2%) when treated with n(DNase). This work demonstrated a general approach for coating matrix-dispersion enzymes to achieve biofilm disintegration and provided a promising strategy for treating biofilm-associated infections.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...