High load drug release systems based on carbon porous nanocapsule carriers. Ibuprofen case study
Abstract
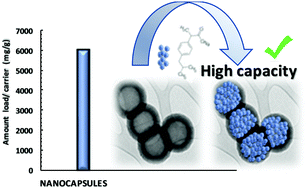
This work shows the application of carbon nanocapsules as carriers for sodium ibuprofen release. Hard templating was used to prepare spherical carbon nanocapsules (mean diameter and thick shell of 690 and 70 nm, respectively), exhibiting both micro and mesoporosity. For comparison purposes, a microporous commercial activated carbon and a home-made mesoporous CMK-3 were also studied. All carbons showed similar drug uptake, although microporous commercial carbon and nanocapsules showed higher uptake at low equilibrium concentration due to higher adsorption potential in micropores. Higher and faster release of sodium ibuprofen was observed for carbon nanocapsules at pH 1.8 and 7.4 for a starting load ca. 250 mg g−1. Subsequent loading of carbon nanocapsules by successive evaporation cycles led to a remarkable load of ca. 6010 mg g−1 thanks to sodium ibuprofen filling the internal void volume. In spite of the very high load a fast release was observed at pH 7.4, reaching a release of ca. 100% of the initial sodium ibuprofen load. However, a much slower and lower release was observed at pH 1.8. Thus, the system developed has interesting features for oral drug administration thanks to low toxicity of porous carbon, low release in gastric medium and important release in intestinal medium.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...