Facile synthesis of monodisperse chromogenic amylose–iodine nanoparticles as an efficient broad-spectrum antibacterial agent†
Abstract
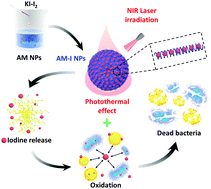
The famous chromogenic reaction between starch and iodine has been widely used for chemical analysis since its first discovery in the year of 1814 while it is seldom utilized in biomedical applications. Inspired by their high iodine content and strong optical absorbance in the near infrared (NIR) region, monodisperse amylose–iodine nanoparticles (AM–I NPs), synthesized by simple mixing of amylose NPs and KI–I2 solutions, were explored as a new class of high-performance antibacterial agent. Benefiting from the broad-spectrum antibacterial property of iodine and photothermal effect of the amylose–iodine complex, the obtained AM–I NPs exhibited an excellent photothermal-enhanced sterilization effect for both Gram-negative Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Gram-positive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). For instance, upon incubation with AM–I NP suspensions (30 μg mL−1) plus NIR laser irradiation (808 nm, 1.33 W cm−2, 5 min), the relative survival rates of E. coli and MRSA were only 1.2% and 1.7%, respectively. In addition, the AM–I NPs depicted better biocompatibility in vitro than that of KI–I2 solution, indicating their safety for potential biomedical applications in vivo. This proof-of-concept study revealed the antibacterial applications of a traditional starch-iodine complex and is expected to provide insights into the design and development of efficient broad-spectrum antibacterial agents.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...