Bioinspired polydopamine nanoparticles: synthesis, nanomechanical properties, and efficient PEGylation strategy†
Abstract
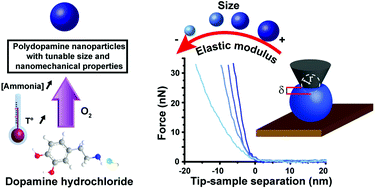
Polydopamine (PDA) is a bioinspired fascinating polymer which is considered nowadays as a material of choice for designing drug delivery nanosystems. Indeed, PDA exhibits multiple interesting features including simple preparation protocols, biocompatibility, simple functionalization procedures, free radicals scavenging and photothermal/photoacoustic properties. However, because of its heterogeneous structure, clear procedures about PDA nanoparticles synthesis and PEGylation with well-defined and reproducible physicochemical properties such as size, shape and nanomechanics are still needed. In this work, we established tightly controlled experimental conditions to synthesize PDA nanoparticles with well-defined size and yield. This allowed us to identify the factors that affect the most these two parameters and to construct surface response plots with accurate predictive values of size and yield. The nanomechanical properties of PDA NPs exhibiting different sizes have been studied with AFM nanoindentation experiments. Our results demonstrated for the first time that the elasticity of PDA NPs was decreasing with their size. This could be explained by the higher geometric packing order of the stacked oligomeric fractions inside the core of the biggest PDA NPs. Next, in order to determine the best PEGylation experimental conditions of PDA NPs using thiol-terminated PEG that allow grafting the highest polymer density with proteins repelling properties, we have first optimized the PEGylation strategy on PDA films. By using a combination of QCM-D and AFM experiments, we could demonstrate that efficient PEGylation of PDA films could be done even at low PEG concentration but in the presence of NaCl which exerts a salting out effect on PEG chains improving thus the grafting density. Finally, we transposed these experimental conditions to PDA NPs and we could synthesize PEGylated PDA NPs exhibiting high stability in physiological conditions as revealed by FTIR and DLS experiments respectively.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...