Flexible and stretchable dual mode nanogenerator for rehabilitation monitoring and information interaction†
Abstract
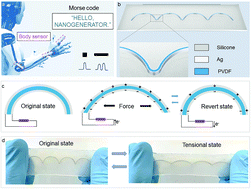
Motion recognition and information interaction sensors with flexibility and stretchability are key functional modules as interactive media between the mechanical motions and electric signals in an intelligent robotic and rehabilitation training system. Nanogenerators have many useful applications in the field of intelligent interaction, with the advantages of a self-powered sensing ability, easy fabrication, considerable sensitivity and reliability. However, the singularity of the sensing mode limits its applications. Hence, in this research, a flexible and stretchable dual mode nanogenerator (FSDM-NG) for human motion sensing and information interaction, based on the integration of piezoelectric and triboelectric principles was developed. In piezoelectric mode, the FSDM-NG can effectively monitor the bending angle of joints (finger, wrist and elbow) from 30° to 90°. In triboelectric mode, text and logic information transfer are encoded using Morse code and logic gates, respectively. In addition, the device has good adhesion and biosafety, and is robust which makes it work normally even in under water environments. Combining these two sensing mechanisms, multiple modes of sensing from touch and stretch based on the FSDM-NG can be achieved for information interaction in real time. The proposed sensor has the potential to be adapted for more complex sensing, which may provide new applications for intelligent interaction of robots and in the rehabilitation training field.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Biosensors


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...