Bifunctional Au-templated RNA nanoparticles enable direct cell uptake detection and GRP75 knockdown in prostate cancer†
Abstract
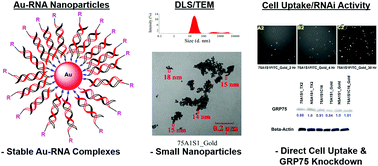
Nucleic acids templated on gold (Au) surfaces have led to a wide range of functional materials ranging from microarrays, sensors and probes in addition to drug delivery and treatment. In this application, we describe a simple and novel method for templating amino-functionalized RNA onto Au surfaces and their self-assembly into small, discrete nanoparticles. In our method, sample hybridization with a complementary RNA strand with and without a fatty acid (palmitamide) appendage produced functionalized double-stranded RNA on the Au surface. The resulting Au-functionalized RNA particles were found to be stable under reducing conditions according to UV-Vis spectroscopy. Sample characterization by DLS and TEM confirmed self-assembly into primarily small (∼10–40 nm) spherical shaped nanoparticles expected to be amenable to cell biology. However, fluorescence emission (λexc: 350 nm, λem: 650 nm) revealed radiative properties which limited cell uptake detection. Introduction of FITC within the Au-functionalized RNA particles produced a bifunctional probe, in which FITC fluorescence emission (λexc: 494 nm, λem: 522 nm) facilitated cell uptake detection, in a time-dependent manner. The dual encapsulation-release profiles of the FITC-labeled Au-functionalized RNA particles were validated by time-dependent UV-Vis spectroscopy and spectrofluorimetry. These experiments respectively indicated an increase in FITC absorption (λabs: 494 nm) and fluorescence emission (λem: 522 nm) with increased sample incubation times, under physiological conditions. The release of Au-functionalized siRNA particles in prostate cancer (PC-3) cells resulted in concomitant knockdown of GRP75, which led to detectable levels of cell death in the absence of a transfection vector. Thus, the formulation of stable, small and discrete Au-functionalized RNA nanoparticles may prove to be valuable bifunctional probes in the theranostic study of cancer cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...