Dual-targeting and excretable ultrasmall SPIONs for T1-weighted positive MR imaging of intracranial glioblastoma cells by targeting the lipoprotein receptor-related protein†
Abstract
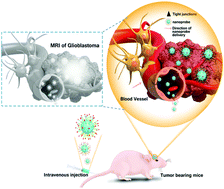
A precise delineation of the intracranial glioblastoma boundary is urgently required for pre-surgical operations, due to the tumor-inherent infiltrative character of a tumor and the difficulty to completely remove the tumor. Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging is the leading clinical diagnostic tool for brain tumors, where a safe MR contrast agent that targets cancer biomarkers is critical for non-invasive and accurate brain tumor detection. In this work, a multifunctional targeted nanoprobe composed of PEGylated ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (USPIONs), with surface conjugated Angiopep-2, was successfully constructed by a stepwise reaction. The nanoprobe efficiently crossed the blood–brain barrier (BBB), targeted the glioblastoma and then generated positive contrast enhancement for T1-weighted MR imaging. Angiopep-2 was herein selected as a targeting ligand to construct the dual-targeting nanoprobes for MR imaging of brain tumors, because it can specifically combine to the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP), which is overexpressed in both BBB and glioblastoma cells. The targeting capability and, in particular, the biocompatibility/excretion of these ANG-modified MRI nanoprobes were systematically evaluated not only at the intracellular level in vitro, but also on tumor xenografts in vivo. This first report on ANG-engineered USPIONs as T1-weighted positive MR contrast agents for intracranial targeted glioblastoma imaging, provides a promising application potential for these SPION-based ultrasmall nanoprobes, not only for efficient pre-operative tumor diagnosis, but also for the targeted surgical resection of intracranial glioblastomas.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...