Investigation of biodistribution and tissue penetration of PEGylated gold nanostars and their application for photothermal cancer treatment in tumor-bearing mice†
Abstract
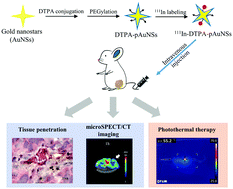
Gold nanostars (AuNSs), with unique physicochemical properties, are thought to be a promising agent for photothermal therapy (PTT). In this study, we prepared PEGylated gold nanostars (pAuNSs) using the HEPES-reduction method. The high photothermal conversion efficiency (∼80%) and photothermal stability of pAuNSs were demonstrated in vitro and in vivo. 111In–DTPA–pAuNSs were prepared as a radioactive surrogate for the biodistribution studies of pAuNSs. In both microSPECT/CT images and the biodistribution study, the tumor-to-muscle (T/M) ratio reached a maximum at 24 h post intravenous injection of 111In–DTPA–pAuNSs. The high linear correlation between the 111In radioactivity and the gold content in the tumors (R2 0.86–0.99) indicated that 111In–DTPA–pAuNSs were appropriate for noninvasively tracking pAuNSs in vivo after systemic administration. Histological examination after silver enhancement staining clearly illustrated that the accumulated pAuNSs in the tumors were mainly located on the luminal surface of vessels. The mice bearing a SKOV-3 xenograft exhibited remarkable therapeutic efficacy with negligible organ damage after receiving pAuNS-mediated photothermal therapy. Our findings suggested that pAuNSs, together with their radioactive surrogate 111In–DTPA–pAuNSs, are promising for applications in image-guided photothermal therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...