High-rate Na0.7Li2.3V2(PO4)2F3 hollow sphere cathode prepared via a solvothermal and electrochemical ion exchange approach for lithium ion batteries†
Abstract
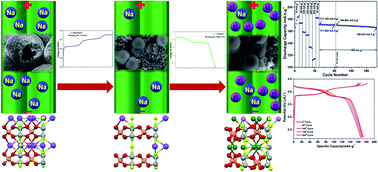
Na3V2(PO4)2F3 (NVPF) has been extensively studied, and has demonstrated excellent electrochemical activity in Na-ion batteries owing to its high reversible specific capacity and stability. The direct chemical synthesis of a Li analogue of NVPF (LVPF) is aided by the high thermodynamic stability of intermediate products. Even more challenging is the synthesis of LVPF with a well-controlled uniform morphology and a stable crystal structure. Herein, an electrochemical ion exchange approach was used to synthesize Na0.7Li2.3V2(PO4)F3 (N0.7L2.3VPF), an isostructural composition of Li3V2(PO4)F3. This compound was prepared via lithiation of Na0.7V2(PO4)F3 with a hierarchical morphology prepared by desodiation of NVPF. We track the phase formation, reversible structural transformation from Pnnm to Cmc21 and back to Pnnm. An initial specific discharge capacity of 185 mA h g−1 and two distinct voltage plateaus visualize the prominence of N0.7L2.3VPF as a cathode material for LIBs. It exhibits a specific discharge capacity of 173, 159, 154, 134 and 114 mA h g−1 at 45, 105, 135, 265, and 535 mA g−1 respectively along with >98% coulombic efficiency, which indicates pronounced electrochemical activity at high current rates due to better diffusivity of smaller Li+ ions than Na+ ions through the partially occupied alkali metal sites in the lattice. Long-term cycling at 45 mA g−1 exhibits 173 mA h g−1 with 96% of capacity retention for 200 cycles. This stable performance further indicates the prominence of N0.7L2.3VPF HMS as a cathode for LIBs. Our findings provide a strategic pathway towards controlling the morphology and crystal structure and shed light on its importance in realization as a cathode material for LIBs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...