Boosting the interface reaction activity and kinetics of cobalt molybdate by phosphating treatment for aqueous zinc-ion batteries with high energy density and long cycle life†
Abstract
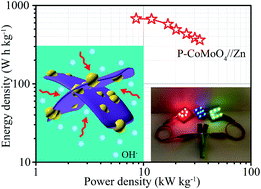
As one of the most reliable power sources for portable and wearable electronics, aqueous zinc-ion batteries fully meet the requirement of high safety, while their energy storage ability is still limited by the lack of high-performance cathode materials. In this study, the poor electrical conductivity and sluggish interface reaction of cobalt molybdate (CoMoO4) nanosheets are well addressed by one-step phosphating treatment (denoted as P-CoMoO4), which serve as an advanced cathode material for rechargeable zinc-ion batteries. Primarily, the electronic structures are finely manipulated using enriched oxygen vacancies, therefore improving the electronic conductivity and reaction activity. Moreover, the modification of surface phosphate ions can reduce the required activation energy for redox reactions and consequently increase the reaction kinetics. Additionally, abundant metallic CoP nanoparticles are uniformly distributed in the matrix of CoMoO4 nanosheets, boosting the exposure of active sites and interface reactions. As expected, the optimized P-CoMoO4 electrode shows a superior specific capacity (431.4 mA h g−1 at 10 A g−1) and rate performance (43.8% capacity retention at 50 A g−1) relative to pristine CoMoO4. Furthermore, the assembled P-CoMoO4//Zn battery exhibits a remarkable energy density of 679.4 W h kg−1 at 8.6 kW kg−1, and an ultra-long life span (over 80% retention of the initial capacity after 12 000 cycles at 60 mV s−1). Hence, this work may offer a preferable option for high-performance cathode materials for aqueous zinc-ion batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...