Optimization of nonatitanate electrodes for sodium-ion batteries†
Abstract
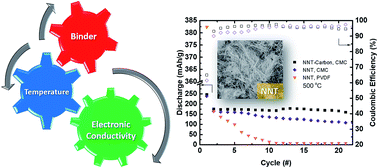
NaTi3O6(OH)·2H2O, also known as “sodium nonatitanate” (NNT) can undergo reversible sodium (de)insertion at low potentials centered around 0.3 V. The low average insertion potential and high theoretical capacity (∼200 mA h g−1 based on site considerations) suggest that it can be a promising high energy density anode material for sodium-ion batteries. However, its low practical capacity, poor capacity retention, and low initial coulombic efficiency require further material and electrode optimization. Herein, the optimization of the material properties of NNT as well as electrode engineering were used to improve these aspects of the electrochemical performance. Characterization tools including pair distribution function analysis, synchrotron X-ray diffraction, and soft and hard X-ray absorption spectroscopy were utilized to probe details of the crystal and electronic structure. Upon drying, rearrangement of the sodium ions in the interlayer space and formation of O–Na–O bridges occur. Hard and soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy show that charge transfer occurs upon discharge of the material in sodium half-cells, consistent with a reversible reductive intercalation mechanism. The best-performing electrodes were dehydrated at 500 °C, and the highest initial capacities of about 200 mA h g−1 were obtained when a CMC binder was used and NNT was carbon-coated. Wrapping NNT with only 1 wt% graphene also resulted in improved performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...