Phase stability and fast ion transport in P2-type layered Na2X2TeO6 (X = Mg, Zn) solid electrolytes for sodium batteries†
Abstract
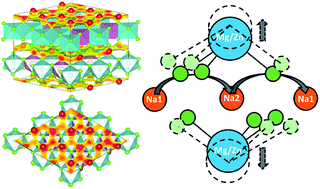
Highly conductive, stable and safe solid-state sodium-ion electrolytes are key components of next-generation sodium batteries for large-scale energy storage. Layered oxide electrolytes are currently attracting great interest because of their unique two-dimensional configuration and facile sodium ion diffusion channels. Using first-principles calculations, we systematically investigated the structural and electrochemical stabilities as well as the sodium ion transport mechanisms in P2-type layered Na2Mg2TeO6 and Na2Zn2TeO6. Both electrolytes display wider intrinsic electrochemical stability windows (1.74–3.15 V and 2.25–3.23 V, respectively) and higher maximum kinetic voltage limits of 3.82 V and 3.57 V compared with sulfides, facilitating electrolyte–electrode compatibility during long-term cycling. Meanwhile, stable passivating interphases will be formed at the interface of Na2Mg2TeO6 or Na2Zn2TeO6 with Na metal, which can significantly extend their electrochemical reduction potentials. The calculated room-temperature sodium ion conductivity of Na2Zn2TeO6 is 9.77 mS cm−1, higher than that of Na2Mg2TeO6 (1.19 mS cm−1), which is mainly due to weaker interactions between sodium ions and the oxide octahedral layers caused by the relatively larger interlayer spacing and softer sodium phonon band center. The low activation energies enable smooth fluid-like sodium ion transport with honeycomb diffusion networks inside the interlayers, exhibiting a collective sodium ion transport mechanism along the preferred Na1–Na3–Na1 diffusion pathway. The ion transport in these layered oxides is found to be correlated with the “switch on/off” vibrational phonon modes of metal oxide octahedra, indicating that tuning the interlayer spacing could help tailor the sodium ion transport in layered oxide electrolytes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...