Custom design of solid–solid phase change material with ultra-high thermal stability for battery thermal management†
Abstract
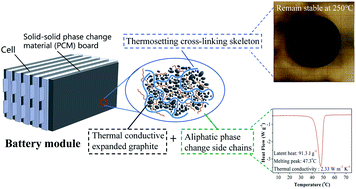
Despite being an advanced battery thermal management (BTM) strategy, the phase change material (PCM) cooling technology still suffers from the low thermal stability of the PCMs in practical applications, which leads to the leakage of the phase change ingredient, shape change or even collapse concerns under high temperature. Here we propose a creative idea for constructing a cross-linked polymeric structure with aliphatic side chains, namely, polymer PCM (PoPCM), through a facile one-step free-radical polymerization of octadecyl acrylate and crosslinkers. The aliphatic chains “tied up” on the cross-linked polymeric skeleton via “chemical bonding” and provided a high latent heat of 98.8 J g−1 without leakage, and therefore, delivered a stable solid–solid phase change behavior during long-term operation. The thermosetting 3-dimensional cross-linked structure simultaneously endowed the PoPCM with the anti-volume-expansion capability and excellent heat tolerance up to 250 °C without any deformation or leakage. When applied for BTM, the solid–solid PoPCM module demonstrated excellent and stable heat dissipation performance. The maximum temperature was 45.3 °C, and the temperature difference of the battery module could be controlled below 3.1 °C during the cyclic charge–discharge tests. Combining with the industrially available reagents and the simple preparation procedure at the kilogram level, we believe that this new strategy can present PCMs with superior feasibility for practical application in BTM.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...