Coexistence of humic acid enhances the reductive removal of diatrizoate via depassivating zero-valent iron under aerobic conditions†
Abstract
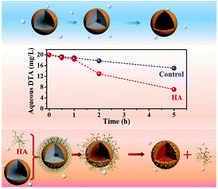
Surface passivation is one of the most challenging aspects in the successful application of zero-valent iron (ZVI) for water decontamination, especially when oxygen is inevitably present. This study found that the coexistence of HA ranging from 0 to 40.0 mg-C/L appreciably improved the pseudo-first-order kinetic rate constant of pollutant diatrizoate (DTA) reduction by ZVI from 0.0454 to 0.1365 h−1 under aerobic conditions. For the first time, it revealed that the coexistence of HA could accelerate the reductive removal of organic contaminants via ZVI surface depassivation rather than the previously proposed electron-shuttle mechanism under aerobic conditions. Interestingly, both DTA removal and Fe0 consumption were found to undergo two stages in the presence of HA, with an initial slight enhancement attributed to the Fe(III)–HA complex formation partially suppressing iron precipitation, followed by a remarkable promotion arising from the HA-associated iron oxide detachment from the Fe0 surface. These findings not only provide a good strategy to enhance ZVI reactivity with minimal extra cost and complexity under aerobic conditions, but also help understand the ZVI behavior in practical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...