Initial investigation and evaluation of potassium metal as an anode for rechargeable potassium batteries
Abstract
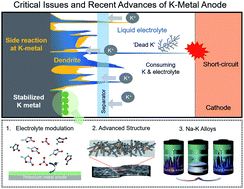
Potassium, the third alkali element after sodium on the periodic table, provides several advantages over lithium and sodium as a charge carrier in rechargeable batteries. Pertaining to its natural features, potassium has a lower standard redox potential than other metallic elements (−2.93 V vs. the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE)) and is highly abundant in the Earth's crust. For these reasons, to date, the development of rechargeable potassium batteries has attracted considerable attention in the search for high-energy and cost-effective energy storage systems. In the development of rechargeable potassium batteries, K metal anodes are the key material and act as the counter electrode to evaluate electrochemical electrode materials in the half-cell configuration. Moreover, they are also an essential component of full-cell potassium–sulfur and potassium–oxygen systems. However, the main hurdle in the widespread acceptance of K metal as an anode in rechargeable potassium batteries lies in identifying fundamental problems and developing suitable solutions. Here, we initially investigate and evaluate potassium metal as an anode for rechargeable potassium batteries and detail the major challenges for K metal systems, that at this time, limit the feasibility of rechargeable potassium batteries, particularly, dendritic growth for liquid systems, poor coulombic efficiency, and the unstable interface between the K metal and electrolyte. In addition, we also highlight the key developments and recent achievements in the stabilization of K metal anodes and their application. This will be helpful in reducing trial and error in studies pertaining to the development of rechargeable potassium batteries and provide crucial insights for potential scientific and industrial applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...