Structural evolution, electrochemical kinetic properties, and stability of A-site doped perovskite Sr1−xYbxCoO3−δ†
Abstract
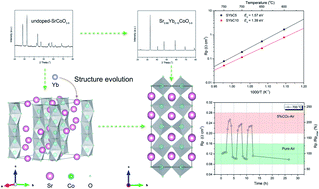
Mixed ionic and electronic conducting (MIEC) perovskite SrCoO3−δ is a widely studied (electro)catalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) and possesses different crystal structures at different temperatures. These temperature dependent phase transitions significantly impact the ordering of oxygen vacancies and electrochemical kinetic properties as well as the reliability of the related devices. Some of the crystal structures formed, e.g. hexagonal phases, turn out to be almost impermeable to oxygen gas. Therefore, it is important to stabilize the crystal structure of SrCoO3−δ that favors the ORR over a wide temperature range. Herein, the partial substitution of the A-site Sr with Yb is systematically studied, including synthesis, characterization and analysis of structural evolution, electrochemical kinetic properties, thermal stability, and stability in a CO2-containing atmosphere. The results indicate that Sr0.90Yb0.10CoO3−δ is able to stabilize the tetragonal crystal structure with less ordered oxygen vacancies, leading to polarization resistances of 0.051, 0.115 and 0.272 Ω cm2 at 750, 700 and 650 °C, respectively, on symmetrical cells. Sr0.90Yb0.10CoO3−δ demonstrates a very stable surface oxygen vacancy distribution and electronic structure near oxygen vacancies but dissociation of adsorbed oxygen molecules into atomic oxygen is affected by surface Sr segregation, and polarization resistance degradation is mainly induced by surface Sr segregation. Furthermore, Sr0.90Yb0.10CoO3−δ exhibits excellent thermal stability as well as excellent recovery stability and improved polarization performance after a few pure air/CO2-containing air treatment cycles at 700 °C. However, a hysteresis behavior of polarization performance is observed at 650 °C during gas cycling treatment, which may cause long-term degradation of the Sr0.90Yb0.10CoO3−δ electrode. The different polarization behaviors during gas cycling treatment are induced by different sensitivities of the formed surface strontium carbonate and chemisorbed surface oxo-carbonaceous species to different operating temperatures.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...