Bismuth doped La0.75Sr0.25Cr0.5Mn0.5O3−δ perovskite as a novel redox-stable efficient anode for solid oxide fuel cells†
Abstract
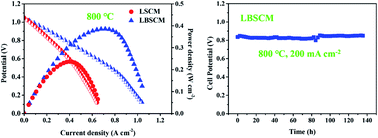
La0.75Sr0.25Cr0.5Mn0.5O3−δ (LSCM) perovskite oxide is a potential ceramic anode material for solid oxide fuel cells. This work aims to improve its catalytic activity for electrochemical anodic reactions by partially replacing lanthanum with bismuth. Bi-doped LSCM is successfully fabricated at 1100 °C in air and is stable in hydrogen at 850 °C although Bi2O3 is not stable under anodic conditions. Bi doping increases the symmetry of the crystal structure, the concentration of surface oxygen species, and the oxygen vacancy concentration associated with the decrease in average Mn valence, and the sinterability meanwhile decreases the electronic conductivity. When single phase LSCM is used as the electrode, Bi doping increases the catalytic activity by a factor of up to 2.2 as determined with symmetrical cells based on perovskite structured electrolytes. The electrode performance is at least 40% higher than those ever reported for LSCM doped with various elements. The performance is even higher than that of LSCM-based composite electrodes and nanostructured composites. In addition, Bi doping increases the peak power density of the electrolyte supported single cell that is from 237 mW cm−2 to 386 mW cm−2 at 800 °C when humidified H2 is used as the fuel and from 119 mW cm−2 to 222 mW cm−2 for syngas fuel. The performance obtained with the single phase anode is about twice as high as those reported with LSCM–YSZ nanocomposite and graded composite anodes. The performance is even higher than that reported with Pd doped (La,Sr)CrO3 where plenty of exsolved Pd nanoparticles function as the electrocatalyst. The performance is competitive with that of widely used Ni-based cermet anodes under similar conditions. Finally, the Bi-doped LSCM based cells show good stability when operated with hydrogen and syngas fuels.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...