A three-dimensional interconnected V6O13 nest with a V5+-rich state for ultrahigh Zn ion storage†
Abstract
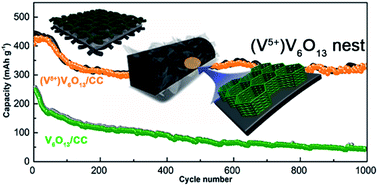
Aqueous zinc ion batteries (ZIBs) have attracted intensive attention due to their low cost, environmental friendliness and high safety. However, exploring suitable cathode materials and a deep understanding of their energy storage mechanisms remain a daunting challenge. In this work, a three-dimensional (3D) nest-like V6O13 structure is grown on carbon cloth (CC) as a free-standing ZIB cathode. Such interconnected V6O13 nanoneedles forming a 3D nest structure provide a large accessible surface area to the electrolyte and rapid channels for Zn2+ diffusion, and V6O13 with a V5+-rich state allows for more possibilities of multielectron reaction upon Zn (de)intercalation. As a result, an aqueous ZIB based on the V6O13/CC cathode and low-cost ZnSO4 electrolyte shows an ultrahigh capacity of 520 mA h g−1 (at a current density of 0.5 A g−1), desirable rate capability and cycle life (showing a stable capacity of 335 mA h g−1 over 1000 cycles). Moreover, the Zn2+ storage mechanism is deeply investigated based on experimental data and density functional theory simulation, and flexible solid-state ZIBs are established based on such a V6O13/CC cathode to reveal its high functional flexibility and excellent electrochemical performance, showing great potential applications in high-performance and safe electronic devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...