Effect of the interfacial protective layer on the NaFe0.5Ni0.5O2 cathode for rechargeable sodium-ion batteries†
Abstract
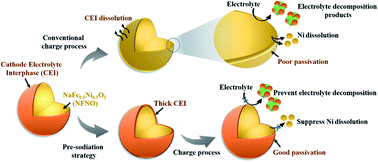
Ni-based cathode materials have received significant attention as advanced electrode materials for sodium-ion batteries (NIBs) due to their high capacities and operating potentials. However, they suffer from rapid capacity fading leading to poor cycling performance, which originates from the side reactions mainly occurring at the cathode–electrolyte interphase (CEI). In this study, to solve the capacity-fading problem, we formed an artificial CEI layer (ACEI) on O3–NaFe0.5Ni0.5O2 (NFNO) through a simple electrochemical pre-discharge step. During the pre-discharge process, the NFNO cathode was electrochemically forced to 1.6 V, which enables the formation of a thin ACEI layer with a thickness of ∼35 nm. We demonstrated that the artificial CEI layer effectively minimizes electrolyte decomposition and prevents transition metal dissolution, thereby improving the interfacial stability of the pre-discharged NaFe0.5Ni0.5O2 cathode. The cyclability of pre-sodiated NFNO could be improved to 86% after 50 cycles, which is far higher than that of pristine NFNO (66%). The pre-sodiation strategy would be a promising and simple way to improve the stability and capacity retention of Ni-based cathode materials for NIBs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...