Carbon-supported Pt5P2 nanoparticles used as a high-performance electrocatalyst for the methanol oxidation reaction†
Abstract
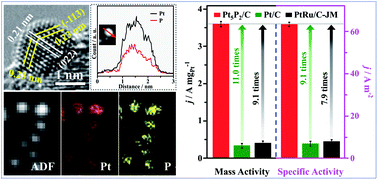
Modification of Pt catalysts to achieve satisfactory activities for commercialization of proton exchange membrane fuel cells has attracted widespread attention in recent years. In this study, a simple one-pot wet-chemical approach for incorporation of phosphorus (P) into Pt to form a supported Pt5P2 alloy phase was developed to enhance the catalytic properties of Pt catalysts toward the methanol oxidation reaction (MOR), including both the activity and durability. The simultaneous use of NaH2PO2 and Na2HPO4 is the most crucial for the formation of the Pt5P2 phase, and the introduction of P results in a smaller size, better dispersion, and the electronic structure change of Pt. The Pt5P2/C catalyst achieves a factor of 11.0 and 9.1 enhancement in mass activity (3.603 A mgPt−1) and specific activity (63.43 A m−2)for the methanol oxidation reaction (MOR) relative to Pt/C, respectively. Moreover, 5000 cycles of the accelerated durability test demonstrated that excellent durability could be obtained for Pt5P2/C, with a drop of 11.8% in mass activity, much smaller than both Pt/C and Pt/C-JM. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report to identify MOR performance on Pt5P2. Given the highly improved catalytic performance, one can anticipate that nanocatalysts composed of Pt and P atoms would shed new light on fuel cells and offer a novel research idea for promoting activity and durability of Pt electrocatalysts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...