Identifying Raman modes of Sb2Se3 and their symmetries using angle-resolved polarised Raman spectra†
Abstract
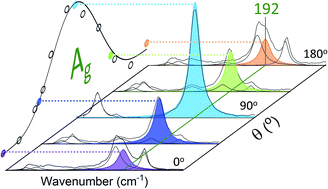
The physical properties of antimony selenide (Sb2Se3) are highly anisotropic. Angle-resolved polarised Raman spectroscopy was employed to characterise oriented crystals and used in conjunction with group theory structural analysis to assign vibrational symmetries to the peaks observed in the Raman spectra. The phonon energies were corroborated via density functional theory (DFT) calculations. Furthermore, a straightforward method is proposed to verify the desirable (001) plane orientation of film growth for device applications via minimisation of the 155 cm−1 peak in the Raman spectrum.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...