Amorphous molybdenum selenide intercalated magnetite as a recyclable trap for the effective sequestration of elemental mercury†
Abstract
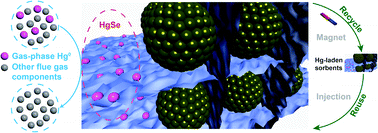
The key to obtaining a cost-effective and environmentally friendly technique for elemental mercury (Hg0) immobilization from industrial flue gases lies in the development of a highly effective and immediately recyclable sorbent that is capable of accommodating volatile Hg0 into a stable mercury species. Amorphous molybdenum selenide intercalating magnetite [MoSex(inter)Fe3O4] was thus purposefully designed in this work to give an ideal response to these challenging requirements. With the assistance of hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide, the active MoSex nanosheets were well intercalated among the Fe3O4 nanoparticles, leading to a structured composite that is beneficial for exerting the Hg0 removal ability of MoSex while also maintaining the magnetization of Fe3O4, allowing it to be easily recycled. Approximately 100% Hg0 removal efficiency was achieved under extremely harsh experimental conditions with gas hourly space velocity (GHSV) and Hg0 concentration values as high as 90 000 h−1 and 500 μg m−3, respectively. The Hg0 adsorption capacity and uptake rate reached approximately 135 mg g−1 and 49 μg g−1 min−1, record-high values compared to previously reported magnetic and recyclable Hg0 sorbents. The recycling tests demonstrated that MoSex(inter)Fe3O4 mixed with large amounts of impurities could be effectively retrieved and reused to adequately exploit the capacity of MoSex(inter)Fe3O4 for Hg0 removal. The dominant product, mercury selenide (HgSe), a mercury species known for negligible environmental leachability, was successfully obtained by the reaction between Hg0 and diselenide (Se22−) in MoSex. This was ascribed to the fact that Se22− played dual roles in the Hg0 immobilization process to simultaneously oxidize Hg0 to Hg2+ and to immobilize Hg2+ to HgSe, a property that distinguished Se22− from monoselenide (Se2−) with no redox capabilities.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...