Nature of terrace edge states (TES) in lower-dimensional halide perovskite†
Abstract
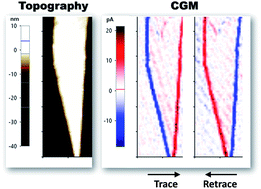
Lower-dimensional quasi-two-dimensional (quasi-2D) halide perovskites have emerged as promising building blocks for multiple optoelectronic applications due to their superior photophysical properties. Recently, there has been a research focus on the terrace edge states (TES) in quasi-2D perovskites, which are thought to provide hypothetical highways to transport the excited states and thus give a new insight into boosting relevant device performance. Nevertheless, there is neither direct evidence of the electronic facets nor an in-depth understanding of these newly observed nontrivial TES. Here, we are the first to directly visualize the highly charged concentrated TES by means of a charge gradient microscopy (CGM) technique and elucidate the nature of TES through a combination of microscopic characterizations, including high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, Kelvin probe force microscopy and confocal fluorescence microscopy coupled with a first-principles density functional theory (DFT) calculation. It is shown that TES of quasi-2D perovskites are highly conductive (in distinct contrast to the insulating flat terrace region) and display a high Fermi-level and small forbidden bandwidth, which is attributed to the unique electron orbitals of the Pb atoms at the terrace edges. This distinctive conductivity of TES is of great importance in distinguishing them from bulk physical properties and inspiring novel nanoscale electronic applications, such as tip-based data storage and triboelectric nanogenerators.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...