Anionic Ln–MOF with tunable emission for heavy metal ion capture and l-cysteine sensing in serum†
Abstract
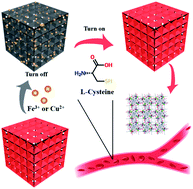
As important biomarkers, the levels of essential amino acids in serum are of vital importance for human health. Here, we reported two sensitive luminescent probes based on a novel heterometallic anionic MOF, Eu–K–bpda (H2bpda = 2,2′-bipyridine-6,6′-dicarboxylic acid), for wide-range L-cysteine detection in serum. Notably, the connected K+ ions enlarged the distance between Ln3+ ions and resulted in a more controllable illuminating color related to the Eu3+/Tb3+ ratio via limiting Tb3+–Eu3+ energy transfer, which has been rarely reported. Benefitting from an anionic framework, MOF exhibited significant adsorption for two heavy metal ions, namely, Fe3+ (105.15 mg g−1) and Cu2+ (143.88 mg g−1) as common toxicant ions with a luminescence response. Therefore, based on the strong affinity between metal ions and L-cysteine, the two designed Fe3+@Eu–K–bpda and Cu2+@Eu–K–bpda could act as efficient turn-on luminescent probes for detecting L-cysteine with high sensitivity (LOD = 0.149 μM) and a wide detection range (0–100 μM). Meanwhile, the luminescent platform demonstrated good water, pH, and thermal stability for recycling. The combination of adsorption and luminescence properties makes Eu–K–bpda a potential functional material for pollution control and biomarker detection.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...