Crown ether modified membranes for Na+-responsive controllable emulsion separation suitable for hypersaline environments†
Abstract
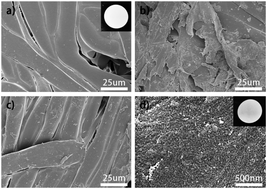
Smart superwetting materials have limited application for oil/water emulsion separation in the ocean due to the hyper-saline environment. Based on this, an ion-responsive material taking advantage of abundant Na+ in the seawater is designed via modifying benzo-15-crown-5 (B15C5) onto a polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) membrane using a facile spray method. Due to the molecular recognition properties of crown ethers, the membrane switches surface wettability based on the complexation between Na+ and B15C5. In a low-salt environment, the membrane exhibits high hydrophobicity (∼145°) and superoleophilicity (0°), which is able to separate various water-in-oil emulsions, while in the marine environment, the membrane changes to be highly hydrophilic (∼20°) and underwater superoleophobic (above 150°), which can be used for the separation of oil-in-water emulsions. A change of dipole distribution in crown ether molecules induces this significant wettability transition. Moreover, the membrane has excellent reusability, high separation efficiency and a facile fabrication process, showing great potential in many fields, such as industrial wastewater treatment under high salt conditions, marine oil-spill cleanup, and fuel purification.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...