Interfacial stability and ionic conductivity enhanced by dopant segregation in eutectic ceramics: the role of Gd segregation in doped CeO2/CoO and CeO2/NiO interfaces†
Abstract
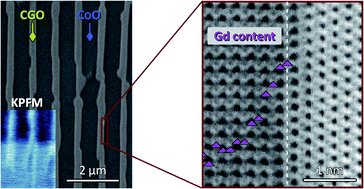
The conductivity of ceramic ionic materials is highly influenced by dopant segregation at the grain boundaries or interfaces, which usually induces a depletion of charge carriers by space charge effects. Hence, obtaining interfacial configurations that promote the formation of oxygen vacancies is highly desirable. In this paper we have combined high resolution electron microscopy (HREM), kelvin probe force microscopy (KPFM) and density functional theory (DFT) to elucidate the equilibrium state of CGO–CoO and CGO–NiO eutectic ceramics (CGO: cerium-gadolinium oxide). HREM proves that the interface is sharp, formed by a single common oxygen plane, and that in CGO–CoO the concentration of gadolinium ions at the interface is almost three times greater than in the bulk, while they distribute homogeneously in the CGO–NiO system. Accordingly, KPFM experiments suggest that interfacial ionic conductivity is much higher in CoO–CGO than in NiO–CGO. DFT demonstrates that Gd segregation in the CGO–CoO reduces the interface energy, contributing to its stability. The Gd-oxygen vacancy complexes compensate the interfacial ionic charge density discontinuity. Additionally, the induced local distortions around the defect release the strain associated with the lattice mismatch. Therefore, we show that in CGO-based eutectics the structure and ionicity of the constituent oxides are essential to promote the interface dopant segregation, indicating a new way to produce nanocomposites with enhanced interfacial ionic conductivity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...