Enhancing the cycle stability of Li–O2 batteries via functionalized carbon nanotube-based electrodes†
Abstract
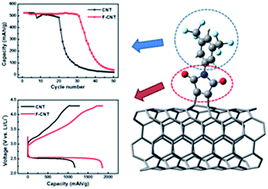
Achieving the high theoretical energy density (∼3500 W h kg−1) of Li–O2 batteries involves maximizing the electrochemically active surface area (EASA) of the electrodes. Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have been widely adopted for Li–O2 electrodes but their EASA is limited by their electrolyte-phobic surface nature and the strong van der Waals interaction between CNTs. To increase the affinity between CNT-based electrodes and the electrolyte without decreasing CNT chemical stability, CNT buckypapers are functionalized with 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenylmaleimide. The solubility parameters of the electrolyte and CNTs are considered so that the maleimide groups increase the affinity between the electrode and electrolyte and the 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl groups protect the maleimide groups from decomposition. The functionalized CNT cathode exhibits a 58% greater discharge capacity and a 50% increased cyclability compared to the pristine CNT cathode when a 1 : 2.5 weight ratio of CNT to electrolyte was used due to an increased EASA and steric hindrance effect. Finally, a 3D folded Li–O2 cell is fabricated using the functionalized CNT-based cathode and demonstrated 30 cycles at 100 W h kgcell−1 cutoff. These results clearly show that high energy density and long cycling performance of Li–O2 batteries can be achieved even with a much reduced amount of electrolyte by increasing the affinity between CNT-based electrodes and the electrolyte.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...