Efficient CsSnI3-based inorganic perovskite solar cells based on a mesoscopic metal oxide framework via incorporating a donor element†
Abstract
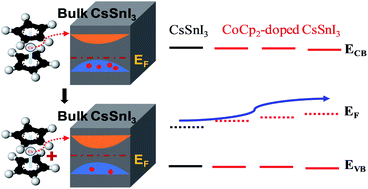
A successful application of perovskite solar cells (PSCs) must face socioeconomic challenges such as lead poisoning. In this regard, Sn-based halide perovskite compounds, such as CsSnI3, have attracted tremendous attention as effective replacements to their counterparts. However, the current CsSnI3 PSCs are still plagued with the tough issues of low efficiency and chemical instability. Herein, for the first time, we present a chemical doping agent, namely, cobaltocene (denoted CoCp2) with a strong electron-donating ability as a stabilizer and an electrical property manipulator of the inorganic CsSnI3 perovskite for photovoltaic applications. A thermal-driven electron injection from CoCp2 into CsSnI3 maintains a reducing environment and thereby effectively suppresses Sn2+ oxidation (named after remote reduction), which can be confirmed by an increase in the density of states near the Fermi level and the emergence of the oxidized species, cobaltocenium (CoCp2+). Therefore, we have achieved an unprecedented efficiency of 3.0% under standard illumination test conditions in air for a perovskite solar cell using a mesoporous TiO2/Al2O3/NiO/carbon framework. We further noticed that without the remote reduction treatment, such devices produced negligible photovoltage and photocurrent. The incorporation of donor elements offers a novel and viable strategy to develop stable Sn-based inorganic PSCs with attractive properties for practical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...