Unravelling the selective growth mechanism of AlOx with dimethylaluminum isopropoxide as a precursor in atomic layer deposition: a combined theoretical and experimental study†
Abstract
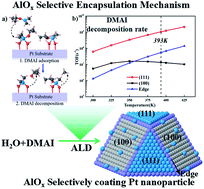
The selective encapsulation of noble metal catalysts is a newly developed method to maintain their durability and reactivity. In our work, we have found that AlOx can preferentially encapsulate Pt nanoparticle facets with dimethylaluminum isopropoxide (DMAI) as an ALD precursor. The selectivity originates from the preferential DMAI decomposition mechanism on double hydroxyl sites of the Pt (111) facet, with the subsequent H2O half cycle rapidly removing residual surface intermediates and regenerating the hydroxyls as reaction sites for subsequent cycles. Related microkinetic and experimental results confirm that by the substitution of one methyl in trimethylaluminum (TMA) with an isopropanol radical, DMAI as the precursor can preferentially coat the Pt (111) facets and leave other sites intact through controlling the ALD deposition parameters. The substituent effect in DMAI is also discussed in detail to give guidance to ALD precursor design. Combining theoretical and experimental studies, our work provides for the first time a feasible strategy to achieve selective decoration of AlOx on Pt nanoparticles via ALD.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...