A phosphorus and carbon composite containing nanocrystalline Sb as a stable and high-capacity anode for sodium ion batteries†
Abstract
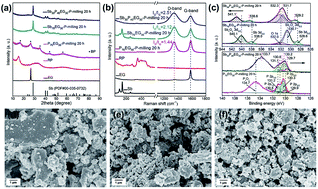
Sodium ion batteries are a potential alternative to lithium ion batteries due to the low cost and natural abundance of sodium. In this study, we demonstrate the synthesis of a ternary Sb/P–C composite by using facile discharge plasma-assisted milling (P-milling) to combine Sb and high theoretical specific capacity red phosphorus (RP). The high hardness Sb particles facilitated the refinement of the P particles and exfoliated expanded graphite during the P-milling process, while the rapid heating by plasma promoted the refinement of Sb and P particles. Ultimately, the crystalline Sb nanograins were well-dispersed in the amorphous P and C matrix, and the P and C components were connected by the P–C bonds. This unique structure ensures a strong electrode structural integrity and ultra-fast electron transport during cycling. As a result, the Sb/P–C composite delivered a high average initial coulombic efficiency of 73.5%, and a reversible capacity of 596 mA h g−1 after 300 cycles at 1.0 A g−1, a very impressive performance among the reported P-based materials. The present approach provides a new strategy for the preparation of anode materials of high capacity and long cycle life for sodium-ion batteries and other energy storage systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...