Abstract
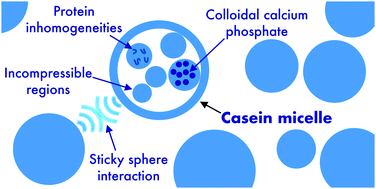
Milk is a ubiquitous foodstuff and food ingredient, and milk caseins are key to the structural properties of milk during processing and storage. Caseins self-assemble into nanometer-sized colloids, referred to as “micelles”, and particles of this size are ideally suited to study by small-angle scattering (SAS). Previous SAS measurements have almost exclusively focussed on the internal structure of the micelles. While important for milk's properties, this attention to the interior of the micelles provides limited information about the structure-forming properties of milk and milk ingredients. The ultra-small-angle X-ray scattering (USAXS) measurements and analysis in this study extend to the micrometer scale, which makes it possible to characterize the interaction between the micelles. Until now, SAS studies have generally excluded a consideration of the interparticle interactions between casein micelles. This is inconsistent with these new data, and it is not possible to model the data without some interparticle attraction. If the micelles are treated as sticky spheres, excellent agreement between experimental data and model fits can be obtained over the length scales studied, from micrometers to ångströms. The stickiness of casein micelles will impact ultra-small-angle scattering and small-angle scattering measurements of casein micelles, but it particularly limits the application of simple approximations, which generally assume that particles are dilute and noninteracting. In summary, this analysis provides an approach to modelling scattering data over many orders of magnitude, which will provide better understanding of interactions between caseins and during food processing.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...