Effects of sea water pH on marine mussel plaque maturation†
Abstract
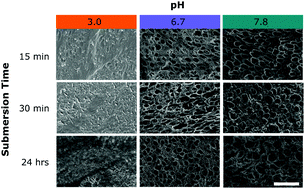
Marine mussel plaques are an exceptional model for wet adhesives. Despite advances in understanding their protein composition and strategies for molecular bonding, the process by which these soluble proteins are rapidly processed into load-bearing structures remains poorly understood. Here, we examine the effects of seawater pH on the time evolution of the internal microstructures in plaques harvested from Mytilus californianus. Experimentally, plaques deposited by mussels on glass and acrylic surfaces were collected immediately after foot retraction without plaque separation from the surface, placed into pH-adjusted artificial seawater for varying times, and characterized using scanning electron microscopy and tensile testing. We found a pH dependent transition from a liquid-like state to a porous solid within 30 min for pH ≥ 6.7; these plaques are load-bearing. By contrast, samples maintained at pH 3.0 showed no porosity and no measurable strength. Interestingly, we found cuticle development within 15 min regardless of pH, suggesting that cuticle formation occurs prior to pore assembly. Our results suggest that sea water infusion after deposition by and disengagement of the foot is critical to the rapid formation of internal structures, which in turn plays an important role in the plaques’ mechanical performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
