Adsorption behaviors of branched cationic gemini surfactants and wettability in quartz–solution–air systems
Abstract
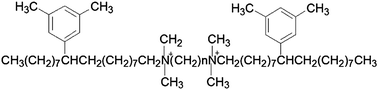
The adsorption and wetting on quartz surfaces by aqueous solutions of xylyl-substituted biquaternary ammonium salt gemini surfactants with different spacer groups (C3 and C6), have been investigated. The interfacial properties of surfactant solutions such as contact angle, adhesional tension (γLV cos θ), quartz–water interfacial tension (γSL) as well as adhesion work (WA) have been estimated. The obtained results show that C3 and C6 have similar adsorption behavior on quartz surfaces. Before critical micelle concentration (cmc) is reached, the contact angles of gemini surfactants slowly increase with the increasing concentration, and the adsorption amount at the water–air interface is almost the same as those at a quartz–water interface. After reaching cmc, the gemini surfactant Cn molecules form a more compact adsorption film through bending the flexible spacer chain, instead of forming a bi-layer. As a result, a further increase in quartz–liquid interfacial tension (γSL) and a consequent increase in contact angle have been observed after cmc. Gemini C6 shows a stronger ability towards hydrophobic modification at a quartz surface than C3, demonstrating the contribution of the longer methylene spacer to the hydrophobic modification of the quartz surface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...