Flower-like droplets obtained by self-emulsification of a phase-separating (SEPS) aqueous film†
Abstract
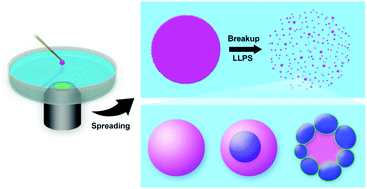
Self-emulsification, referring to the spontaneous formation of droplets of one phase in another immiscible phase, is attracting growing interest because of its simplicity in creating droplets. Existing self-emulsification methods usually rely on phase inversion, temperature cycling, and solvent evaporation. However, achieving spatiotemporal control over the morphology of self-emulsified droplets remains challenging. In this work, a conceptually new approach of creating both simple and complex droplets by self-emulsification of a phase-separating (SEPS) aqueous film, is reported. The aqueous film is formed by depositing a surfactant-laden aqueous droplet onto an aqueous surface, and the fragmentation of the film into droplets is triggered by a wetting transition. Smaller and more uniform droplets can be achieved by introducing liquid–liquid phase separation (LLPS). Moreover, properly modulating quadruple LLPS and film fragmentation enables the creation of highly multicellular droplets such as flower-like droplets stabilized by the interfacial self-assembly of nanoparticles. This work provides a novel strategy to design aqueous droplets by LLPS, and it will inspire a wide range of applications such as membraneless organelle synthesis, cell mimics and delivery.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...