Investigating the role of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) in the piezoelectric performance of a PVDF/KNN-based electrospun nanogenerator
Abstract
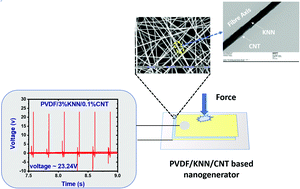
In the present study, the effect of varying the concentration of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) on the piezoelectric performance of a poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF)/potassium sodium niobate (KNN)-based electrospun nanocomposite has been revealed. The incorporation of 0.1% CNTs in the PVDF/KNN composite results in a significant improvement in the performance of the nanogenerator, with an output voltage of ∼23.24 V, a current of ∼9 μA and a power density of 52.29 μW cm−2 under finger tapping compared with a voltage of ∼12 V, a current of ∼18 μA and a power density of 54 μW cm−2 upon the application of a mechanized compressive force. In fact, the addition of CNTs led to a higher β-fraction in the hybrid nanocomposite. Moreover, the presence of CNTs creates a conducting path in the nanofiller loaded polymer jet, which results in enhanced mechanical stretching of the electrospun fibres. This hybrid lead-free nanogenerator could be a good candidate for use in self-powered portable and wearable electronic goods where a very small amount of power is required.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...