Fractional viscoelastic models for power-law materials†
Abstract
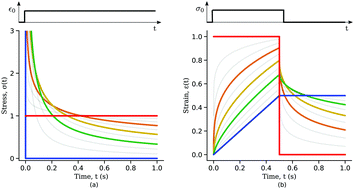
Soft materials often exhibit a distinctive power-law viscoelastic response arising from broad distribution of time-scales present in their complex internal structure. A promising tool to accurately describe the rheological behaviour of soft materials is fractional calculus. However, its use in the scientific community remains limited due to the unusual notation and non-trivial properties of fractional operators. This review aims to provide a clear and accessible description of fractional viscoelastic models for a broad audience and to demonstrate the ability of these models to deliver a unified approach for the characterisation of power-law materials. The use of a consistent framework for the analysis of rheological data would help classify the empirical behaviours of soft and biological materials, and better understand their response.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...