Controlled shape morphing of solvent free thermoresponsive soft actuators†
Abstract
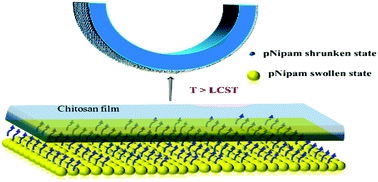
High performance thermoresponsive soft, controllable and reversible actuators are highly desirable for diverse applications. The practical implementation of the existing poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (pNipam) based soft thermoresponsive actuators faces serious limitations due to their functional requirement of proximal bulk solvent medium. In this work, addressing this issue, we report the development of a bilayer based actuator composed of a solvent responsive biodegradable polymer and temperature responsive pNipam. The designed bilayer is capable of achieving reversible and irreversible actuation as needed when exposed to a physiological range of body temperature, without any solvent bath around. The solvent or water supplied by the pNipam layer at its lower critical solution temperature (LCST) builds a concentration gradient across the thickness of the polymer layer. The concentration gradient results in a strain gradient, causing an out-of-plane folding of the bilayer. The underlying coupled diffusion–deformation interaction during folding and unfolding is incorporated in the reported finite element model, capable of predicting actuation characteristics under different initial conditions. The combined experimental and modelling effort in this work highlights the possibility of engineering 2-dimensional films into complex 3-dimensional shapes, which could have potential applications in soft machines and robotics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...