Kinetics of albumin microbubble dissolution in aqueous media†
Abstract
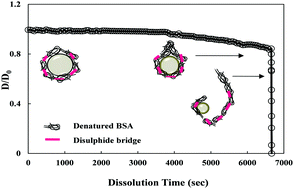
The effectiveness of microbubbles as ultrasound contrast agents and targeted drug delivery vehicles depends on their persistence in blood. It is therefore necessary to understand the dissolution behavior of microbubbles in an aqueous medium. While there are several reports available in the literature on the dissolution of lipid microbubbles, there are no reports available on the dissolution kinetics of protein microbubbles. Moreover, shell parameters such as interfacial tension, shell resistance and shell elasticity/stiffness which characterize microbubble shells, have been reported for lipid shells but no such data are available for protein shells. Accordingly, this work was focused on capturing the dissolution behavior of protein microbubbles and estimation of shell parameters such as surface tension, shell resistance and shell elasticity. Bovine serum albumin (BSA) was used as a model protein and microbubbles were synthesized using sonication. During dissolution, a large portion of the protein shell was found to disengage from the gas–liquid interface after a stagnant dissolution phase, leading to a sudden disappearance of the microbubbles due to complete dissolution. In order to estimate shell parameters, microbubble dissolution kinetic data (radius vs. time) was fit numerically to a mass transfer model describing a microbubble dissolution process. Analysis of the results shows that the interfacial tension increases drastically and the shell resistance reduces significantly, as protein molecules leave the gas–liquid interface. Furthermore, the effect of processing conditions such as preheating temperature, microbubble size, and core gas and shell composition on the protein shell parameters was also evaluated.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...