Synthesis and effective catalytic performance in cycloaddition reactions with CO2 of boronate esters versus N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC)-stabilized boronate esters†
Abstract
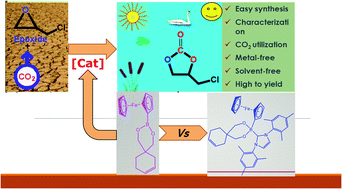
A series of boronate esters (1–3) and N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC)-stabilized boronate esters (4–6) were synthesized and characterized by various spectroscopic techniques, including NMR (1H, 13C, and 11B), FT-IR, UV-Vis, LC-MS/MS spectrometry, melting point, and elemental analysis techniques. The boronate esters (1–3) and N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC)-stabilized boronate esters (4–6) (as Lewis acid) rapidly catalyze the coupling of a variety of epoxides and CO2 to obtain cyclic carbonates in the presence of DMAP (as Lewis base) without the organic solvent. Good to excellent yields of various cyclic carbonates were also achieved under suitable conditions (125 °C, 0.5 h, and 1.6 MPa). After seeing the high catalytic performance of boronate ester catalysts, effects of epoxide, base, temperature, CO2 pressure, reaction time and amount of catalyst and base were investigated for these catalysts. The boronate ester (1) and DMAP showed the best catalytic activity (94.3%) and selectivity (97.5%) for the coupling of CO2 and ECH under suitable conditions (125 °C, 0.5 h, and 1.6 MPa).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...