Cobalt(ii) ions and cobalt nanoparticle embedded porous organic polymers: an efficient electrocatalyst for water-splitting reactions†
Abstract
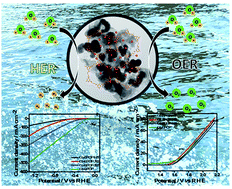
Development of a highly efficient electrocatalyst for the water-splitting reaction is essential and in this regard, the use of earth-abundant metal catalysts offers several advantages such as improved performance, cost-efficiency, etc. Recent studies have shown that the fabrication of transition metal/metal oxide nanoparticle supported carbon materials exhibit similar performances to that of bare metal/metal oxide nanoparticles. Herein, we report the preparation of an ethylenediamine interconnected triazine based porous organic polymer (EPOP) modified with Co2+ (Co-EPOP) and Co nanoparticles (Co-EPOP-300, Co-EPOP-500 and Co-EPOP-HT) via anchoring under different conditions. The amine groups on the EPOP polymer were used as ligands and as stabilizers for Co2+ and Co nanoparticles respectively. XRD and TEM analysis indicated that the Co-NPs covered a homogeneous polymer matrix. The electrocatalytic activities of Co2+/CoNP modified POPs were evaluated under standard OER and HER conditions and were compared with that of Co-NPs without polymer support. Amongst the electrocatalysts, the Co-EPOP (Co2+ anchored EPOP) sample exhibited bifunctional activity towards both the OER and HER with onset potentials of 1.638 and −0.173 V respectively. Further, the Co-EPOP catalyst showed lower Tafel slope values compared to other catalysts. Both OER and HER performances are comparable with those of reported Co based nanocatalytic systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...