Study on boron-containing electrolytes at extra-high temperatures for lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
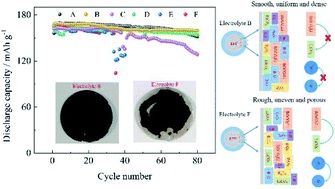
Broadening the temperature range of lithium-ion batteries can be achieved by optimizing the composition of lithium salts in the electrolyte, which is currently one of the most popular methods. In this study, we report an extra-high temperature electrolyte by optimizing the proportion of mixed lithium salts (LiBOB and LiBF4) with ethylene carbonate (EC), diethyl carbonate (DEC) and ethyl methyl (EMC) as an equal volume mixture. An extra-high temperature of 75 °C is applied in a half cell with lithium iron phosphate (LFP) as the cathode and a lithium foil as the anode. The cycle stability and rate performance of the cell with various electrolytes based on mixed lithium salts are systematically investigated and a comparison of the polarization and impedance characteristics is conducted as well. The most outstanding electrolyte composition is electrolyte B (0.6 M LiBOB + 0.1 M LiBF4-EC/DEC/EMC). The optimized electrolyte not only maintains good cycle stability (the capacity retention rate is 98% after 80 cycles) and excellent rate performance at the extra-high temperature, but also minimizes the polarization during cycling, which is mainly due to the formation of a dense and smooth cathode electrolyte interface (CEI) film, as observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The CEI film that contains B–O bonds and organic components is systematically analyzed by energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), which shows that the components aid the extra-high temperature cycling stability of the cell. Our data indicate that the composition of lithium salts in the electrolyte is pivotal to the properties of the CEI film, which largely determines the performance of the cell at extra-high temperatures. The conclusions of this work can contribute significantly to the application of extra-high temperature electrolytes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...