Carbon nanosheets from biomass waste: insights into the role of a controlled pore structure for energy storage†
Abstract
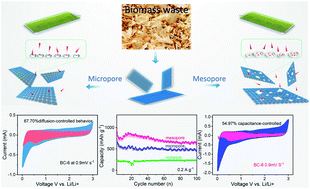
Due to their excellent physical and chemical stability and long-term cycling, insertion anodes are becoming increasingly important in energy storage. However, insertion anodes still suffer from low energy density and large irreversible capacity. Systematically controlling the macroscopic structure and microscopic crystal parameters are effective ways of improving the energy density, cycle capacity, and rate performance of carbonaceous materials. In this work, a series of nonporous, microporous, and mesoporous carbon nanosheets was designed and fabricated from balsa waste by thermal infiltration, and displayed high disorder and abundant surface functional groups. The sample with the best performance (BC-8) had a large pore size centred at 2.5–4.5 nm, accompanied by a highly disordered crystallite structure, expanded carbon interlayers, a large number of active sites, and small particle sizes. The results revealed that mesoporous carbon nanosheets deliver a large capacity, and that the ion storage capacity of carbon nanosheets could be increased by optimizing the pore size. As an ion storage anode, sample BC-8 exhibited higher reversible capacity (630 mA h g−1 at a rate of 0.2 A g−1 after 100 cycles), longer cycling stability, and better rate performance (150 mA h g−1 at 5 A g−1 after 1000 cycles) than the other samples. Kinetic analysis confirmed that porous carbon nanosheet materials show a synergistic effect between capacitor-like and diffusion-controlled behavior; the excellent electrochemical properties of mesoporous carbon nanosheets are dominated by diffusion-controlled behavior; and the capacity of the micropores is mainly governed by surface capacitance-controlled contributions. Our work helps explain the improved ion storage behavior of carbon with a two-dimensional nanosheet structure and provides an effective strategy for designing higher energy density carbon materials for advanced energy storage systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...