An in situ cross-linked vinylphosphonic acid-modified aminosilicon oxide gel electrolyte for proton exchange membrane fuel cells†
Abstract
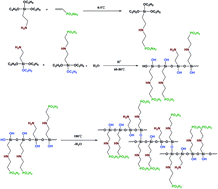
Highly conductive and water-retentive vinylphosphonic acid-modified aminosilicon oxide cross-linked polymer/perfluorosulfonic acid (VPA-ASOCP/PFSA) membranes were prepared using PFSA solution and vinylphosphonic acid-modified (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane (VPA-APTES) as precursors. Spectroscopic and Energy Dispersive Spectrometer (EDS) analyses revealed that in situ generation of a VPA-ASOCP network was effectively achieved along with homogeneous dispersion of silicon backbones and phosphonic acid groups in the PFSA matrix. These composite membranes exhibited an increased water uptake and associated better conductivity at low and medium relative humidity (RH) compared to a pristine PFSA membrane and commercial Gore 740 membrane. The proton conductivity results showed that the VPA-ASOCP/PFSA composite membrane provided a proton conductivity of up to 24 mS cm−1 at 30% RH and 12.4 mS cm−1 at 10% RH, which were respectively 4.8 times and 10.3 times higher than those of the PFSA membrane and 4.5 times and 6.8 times higher than those of the commercial Gore 740 membrane on its own. In addition, the VPA-ASOCP/PFSA composite membrane exhibited superior fuel cell performance and low ohmic resistance across the entire humidity range for fuel cell operation, and the VPA-ASOCP/PFSA composite membrane provided a cell voltage as high as 0.672, 0.664, and 0.648 V at a current density of 1.0 A cm−2 when the RH was 50%, 20%, and 0, which were 50, 71 and 90 mV higher than those of the PFSA membrane and 34, 50 and 72 mV higher than those of the Gore 740 membrane. The water transport and small-angle X-ray scattering experimental results demonstrated that water transport was enhanced and new proton transport channels were formed when the VPA-ASOCP/PFSA composite was used as a proton exchange membrane (PEM). This new type of VPA-ASOCP/PFSA composite membrane is promising for developing PEMs that tolerate variations in humidity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...