Reversible photoactivation in coordination polymer-derived CdS/Co–N species composites for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution†
Abstract
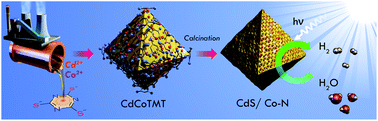
The reversible activation process, which involves electron transfer from adjacent redox mediators to cofactors, the reversible chemical state change of cofactors, and the functional/structural change of redox mediators, is one of the most significant features of biological enzymes, and has inspired the design of homogeneous catalysts. However, for heterogeneous catalysts, such enzyme-like characteristics have been only observed in very few transition metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) and single copper atom incorporated TiO2 catalysts during dynamic photocatalytic processes, and have never been seen in industrially important visible light-driven narrow-band gap semiconductor catalysts. Herein, we first report on the design and synthesis of highly active CdS/Co–N redox catalysts through the pyrolysis of trithiocyanuric acid cadmium-cobalt (CdCoTMT) coordination polymers as single-source precursors, which exhibit a reversible photoactivation process. This unique design and synthetic strategy provide a platform that facilitates atomic-level anchoring control of cofactor transition metal atoms (Co2+ and Ni2+), reversible modulation of the macroscopic optoelectronic properties of CdS and enhancement of photocatalytic hydrogen evolution, promoting the practical application of conventional heterogeneous catalysts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...