Structural reduced graphene oxide supercapacitors mechanically enhanced with tannic acid†
Abstract
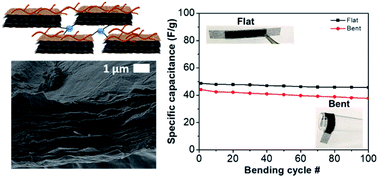
Electrodes that combine energy storage with mechanical performance are desirable for structural and flexible applications. However, conventional electrodes fail to address mechanical performance. Here, noncovalent bonding of graphene/aramid nanofiber electrodes with tannic acid yields a significant improvement in tensile strength and Young's modulus while maintaining good energy storage.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...