Vapor-fed photoelectrolysis of water at 0.3 V using gas-diffusion photoanodes of SrTiO3 layers†
Abstract
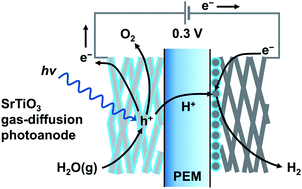
Large scale production of H2 using renewable energy can be realized by photoelectrochemical (PEC) splitting of water vapor in the gas phase. Air humidity can be a water source for producing solar H2. The concept is based on photoelectrochemistry in a gaseous environment using a proton exchange membrane (PEM) as a solid polymer electrolyte and a macroporous semiconductor electrode wrapped in a perfluorosulfonic acid ionomer. A prototype vapor-fed PEC cell using a TiO2 gas-diffusion electrode as an O2-evolving photoanode and a carbon-supported platinum catalyst cathode achieved water splitting to produce O2 and H2, which are physically separated from each other by the PEM. Herein, we demonstrate a PEM-PEC system consisting of a strontium titanate (SrTiO3) nanocrystalline layer decorated on titanium microfiber felt to achieve overall water splitting into H2 and O2 at a ratio of 2 : 1 on each electrode at an applied voltage of only 0.3 V under gaseous conditions. In comparison with TiO2 electrodes, the SrTiO3 gas-diffusion electrode decreased the external voltage and suppressed the gradual decomposition of the ionomer coated on the photoanode. These differences are because of the cathodic shift of the photocurrent onset potential and improvement of the Faraday efficiency of O2 evolution, respectively. The interface between the SrTiO3 surface and the ionomer thin film exhibited fast kinetics for O2 evolution from water adsorbates supplied from the gas phase and durability under ultraviolet light irradiation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
