Engineering of electrodeposited binder-free organic-nickel hydroxide based nanohybrids for energy storage and electrocatalytic alkaline water splitting†
Abstract
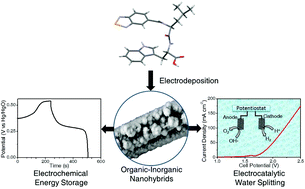
Organic–inorganic nanohybrids are widely used as electrode materials for various applications due to their high conductivity with porosity and tuneable nanostructures. However, the poor stability of organic–inorganic hybrid materials in aqueous alkaline electrolytes and the presence of binders restrict their use in various electrochemical applications such as energy storage and electrocatalytic water splitting. A class of electrodeposited binder-free organic–inorganic hybrid materials based on a benzo[2,1,3]selenadiazole-5-carbonyl N-capped dipeptide (BSeLW) and metal hydroxide (Ni(OH)2) are prepared for electrochemical applications. The binder-free electrodeposited nanohybrids grown on carbon paper (CP) ((1 : 20) BSeLW/Ni(OH)2/CP) are stable in aqueous 1 M KOH electrolyte solution and exhibit pseudo-capacitive behavior with a high charge storage efficiency of 742 F g−1 at 1.5 A g−1. A prominent 71% specific capacitance retention at 10 A g−1 after 1000 cycles indicates higher stability of dipeptide-based organic–inorganic nanohybrids on the carbon paper-based electrode surface. Additionally, the nanohybrid shows catalytic activity for electrocatalytic water splitting with a low overpotential for the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) and hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) in alkaline aqueous 1 M KOH solution. This work elucidates the rational engineering of organic–inorganic binder-free multi-functional nanohybrid electrodes as a favorable candidate for high-performance energy storage and electrocatalyst for electrocatalytic water splitting.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...