Rhodium catalysed C-3/5 methylation of pyridines using temporary dearomatisation†
Abstract
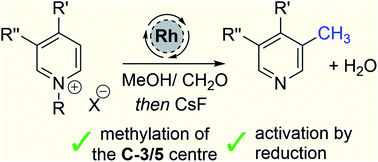
Pyridines are ubiquitous aromatic rings used in organic chemistry and are crucial elements of the drug discovery process. Herein we describe a new catalytic method that directly introduces a methyl group onto the aromatic ring; this new reaction is related to hydrogen borrowing, and is notable for its use of the feedstock chemicals methanol and formaldehyde as the key reagents. Conceptually, the C-3/5 methylation of pyridines was accomplished by exploiting the interface between aromatic and non-aromatic compounds, and this allows an oscillating reactivity pattern to emerge whereby normally electrophilic aromatic compounds become nucleophilic in the reaction after activation by reduction. Thus, a set of C-4 functionalised pyridines can be mono or doubly methylated at the C-3/5 positions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...